In modern manufacturing, automation, robotics, and various precision equipment, high-precision motion control is a core performance indicator. Precision linear guides are the key components that enable these devices to achieve efficient, stable, and low-friction linear motion.
1. What are Precision Linear Guides?
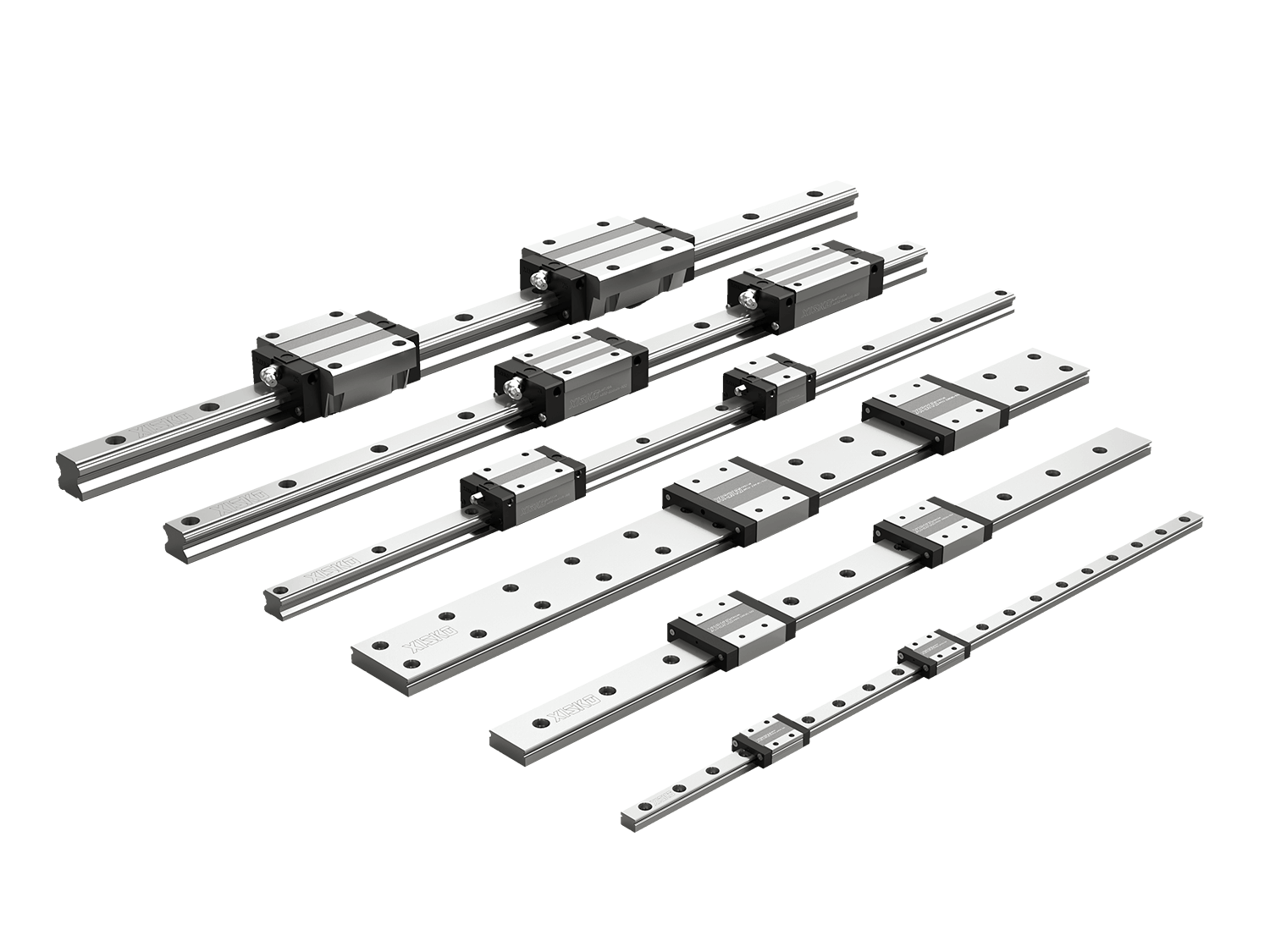
Precision linear guides are mechanical transmission components used to provide high-precision linear motion guidance. They typically consist of three parts:
Guide rails: Mounted on the equipment base, they serve as the track on which the sliders run;
Sliders: Slide freely along the guide rails, connecting the moving parts;
Rolling elements: such as balls or rollers, sit between the guide rails and sliders, bearing loads and enabling low-friction sliding.
Through the coordinated operation of these components, precision linear guides achieve smooth, repeatable, and highly accurate linear motion within specified limits with minimal friction. They are widely used in applications such as CNC machine tools, laser cutting equipment, semiconductor devices, and medical instruments.
2. Advantages
2.1 High positioning accuracy
When using linear guides as linear guides, since the linear guides use rolling friction, not only is the friction coefficient reduced to 1/50 of that of sliding guides, but the difference between dynamic friction and static friction also becomes very small. Therefore, when the bed is running, there will be no slipping, and the positioning accuracy of um level can be achieved.
2.2 Low wear and long-term accuracy maintenance
Traditional sliding guides will inevitably cause poor platform movement accuracy due to the backflow of the oil film, and insufficient lubrication during movement. This will cause wear on the contact surface of the running track, seriously affecting the accuracy. However, the wear of rolling guides is very small, so the machine can maintain accuracy for a long time.
2.3 Suitable for High-Speed Movement
Since the friction of the linear guide is very small when moving, only a small amount of power is required to make the bed run, especially when the bed works in a regular back-and-forth operation, which can significantly reduce the power loss of the machine. Because the heat generated by friction is small, it is suitable for high-speed operation.
2.4 Can Bear Multi-Directional Loads at the Same Time
Due to the special beam structure design of the linear guide, it can bear loads in the up, down, left and right directions at the same time. Unlike the sliding guide, which can bear lighter lateral loads in the parallel contact surface direction, it is easy to cause poor machine operation accuracy.
2.5 Easy to Assemble and Interchangeable
During assembly, just mill or grind the assembly surface of the slide on the machine and fix the slide and slider to the machine with a specific torque according to the recommended steps to reproduce the high precision during processing. Traditional sliding guides require scraping the running track, which is both troublesome and time-consuming. Once the machine accuracy is poor, it must be scraped again. Linear guides are interchangeable. The slider or slide or even the linear guide group can be replaced separately, and the machine can regain high-precision guidance.
2.6 Simple Lubrication Structure
If the sliding guide is not lubricated enough, it will cause direct friction wear of the metal on the contact surface. However, it is not easy to lubricate the sliding guide sufficiently. It is necessary to drill holes in the appropriate position of the bed to supply oil. The linear slide has an oil nozzle installed on the slider. The grease can be directly injected with a grease gun, or a special oil pipe joint can be replaced to connect the oil supply pipe and lubricate it with an automatic oil supply machine.
3. Working Principle of Precision Llinear Guide
Precision linear guide adopts rolling friction motion:
When the slider moves on the guide rail, the ball (or roller) rolls between two precision-machined grooves, and the rolling body rolls back and forth between the slider and the guide rail. This rolling contact greatly reduces the wear and energy consumption caused by traditional sliding friction.
Core Features
High positioning accuracy and repeatability: The rolling mechanism ensures smooth and consistent movement;
Low friction resistance: Suitable for high-speed movement and precise positioning;
High rigidity load-bearing capacity: Can withstand loads in multiple directions;
Achieve micron-level control: Suitable for high-end precision processing needs.
Summary
Precision linear guide system is an indispensable core component for achieving high-performance mechanical movement. As demand for industrial automation and high-precision manufacturing continues to grow, the application scope of precision guide rail systems will become increasingly extensive.