In modern manufacturing, CNC machine tools are core equipment for high-precision machining and high-efficiency production. One of the key motion components supporting their stable operation, high-speed positioning, and repeatable machining accuracy is the linear rail actuator. This article will delve into the role, advantages, and typical applications of linear guide actuators in CNC machine tools to help you better understand their central role in industrial automation.
1. What is a Linear Rail Actuator?
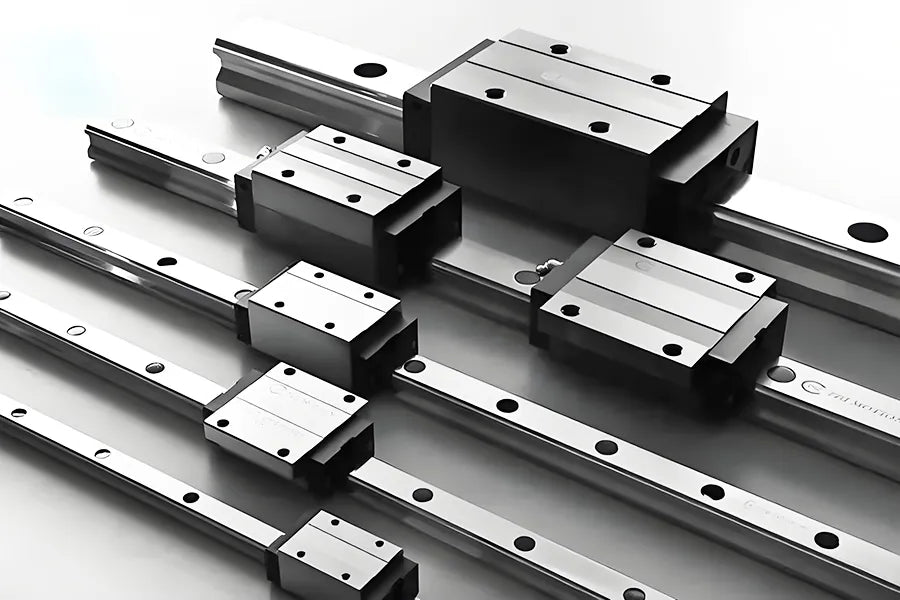
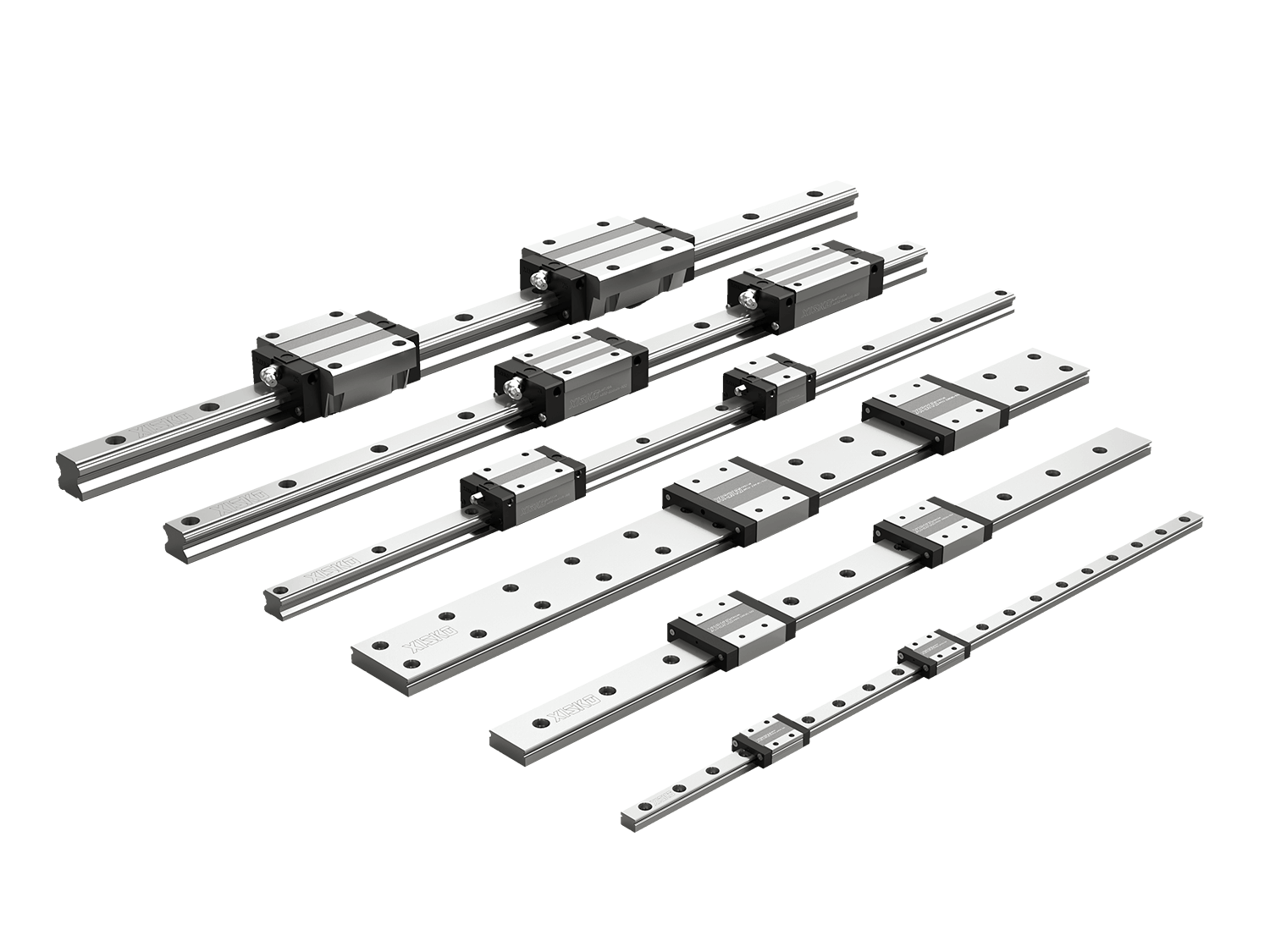
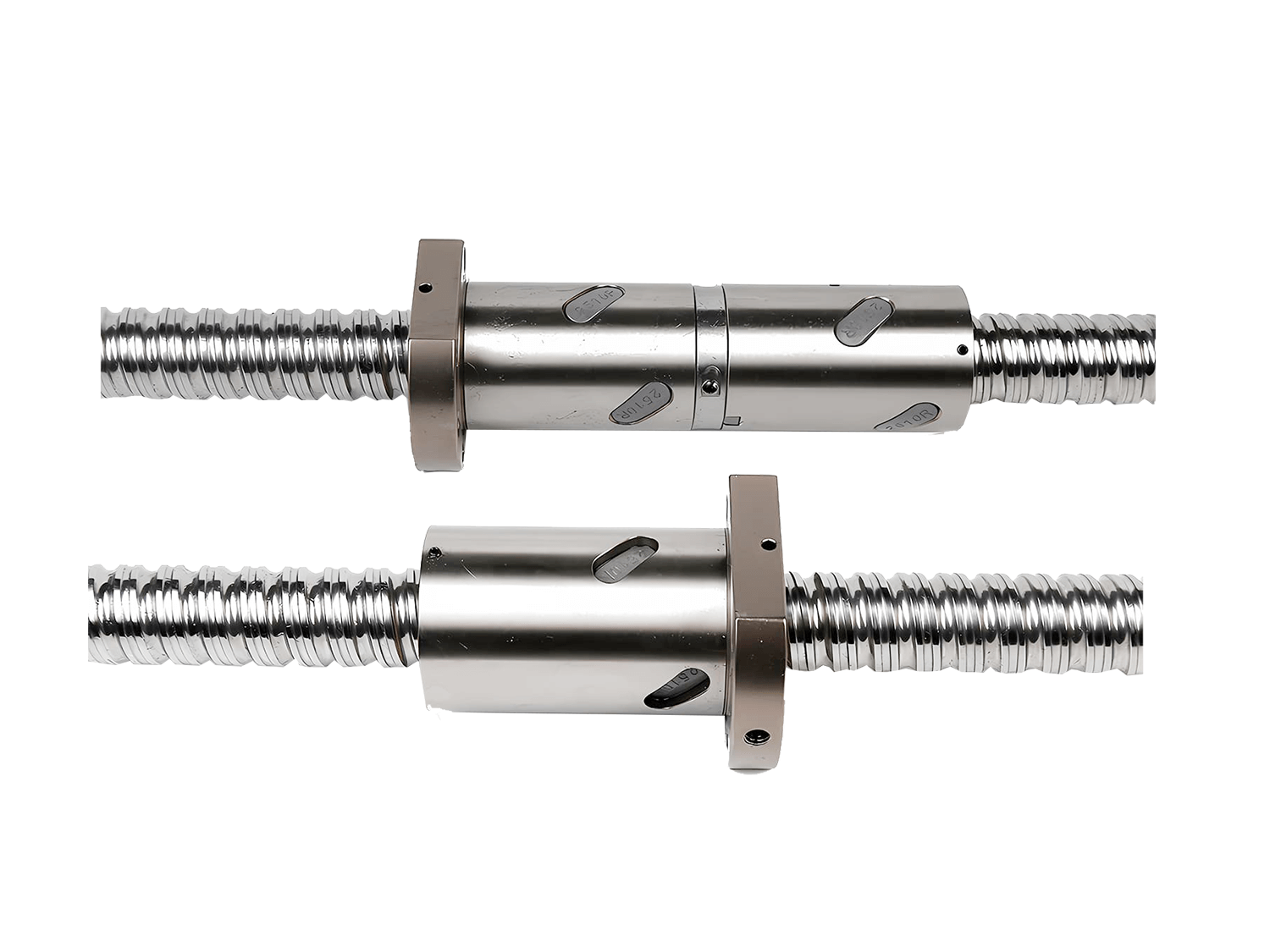
A linear guide actuator is a linear motion module that integrates a linear guide system with a drive device (such as a ball screw, belt, or linear motor).
It achieves stable, controllable, and low-friction reciprocating motion while maintaining high load, high rigidity, and high precision.
In CNC machine tools, actuators are often used to control the position of the worktable (X/Y/Z axes), tool holder, or spindle slide. They are the core mechanism for positioning, feed, rapid retraction, and interpolation motion.
2. Typical Applications
2.1 X/Y/Z Three-Axis Positioning System
CNC machine tools typically rely on corresponding linear rail actuators to drive the worktable and spindle for three-axis machining:
X-axis: Moves the workpiece left and right;
Y-axis: Moves the workpiece forward and backward;
Z-axis: Moves the spindle up and down.
The positioning accuracy of these axes directly determines the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the workpiece.
2.2 Automatic Tool Changer (ATC)
Some tool magazines or tool changers use short-stroke linear rail actuators to achieve fast and stable linear motion, such as pushing a tool from the magazine into the spindle.
2.3 Automatic Workpiece Loading and Unloading Platforms
Auxiliary systems used for automated workpiece loading and unloading, handling, and alignment often require the coordinated operation of slide-type or multi-axis linear modules.
2.4 Spindle Slide and Column Lift Systems
Large gantry milling machines, horizontal machining centers, and other equipment require heavy-duty linear actuators to drive the vertical or horizontal movement of the spindle or machining head.
3. Advantages of Linear Rail Actuators
3.1 High Precision and High Repeatability
The ball screw combined with a precision guide rail design achieves submicron repeatable positioning.
Suitable for the stringent requirements of high-end CNC equipment for "inch-to-inch accuracy."
3.2 High Integration and Easy Installation
Compared to the traditional "guide rail + lead screw + motor" structure, modular actuators offer a high degree of integration.
This reduces installation errors and improves overall mechanical performance.
3.3 High Rigidity and High Load Capacity
The high-rigidity slider and fully supported structure withstand complex working conditions such as cutting forces and inertial shock.
Particularly suitable for heavy-load systems such as vertical machining centers and gantry milling machines.
3.4 Customizable and Flexible Expansion
Offering various strokes, speeds, and load ratings based on customer needs.
Supporting integration with rotary axes, multi-axis stages, sensors, and vision systems.
Summary
In the field of CNC machine tools, linear rail actuators are not only a fundamental transmission component but also the core actuator that enables high-precision and high-efficiency machining. Its precision, stability and reliability directly determine the operating quality and production level of the entire machine tool.