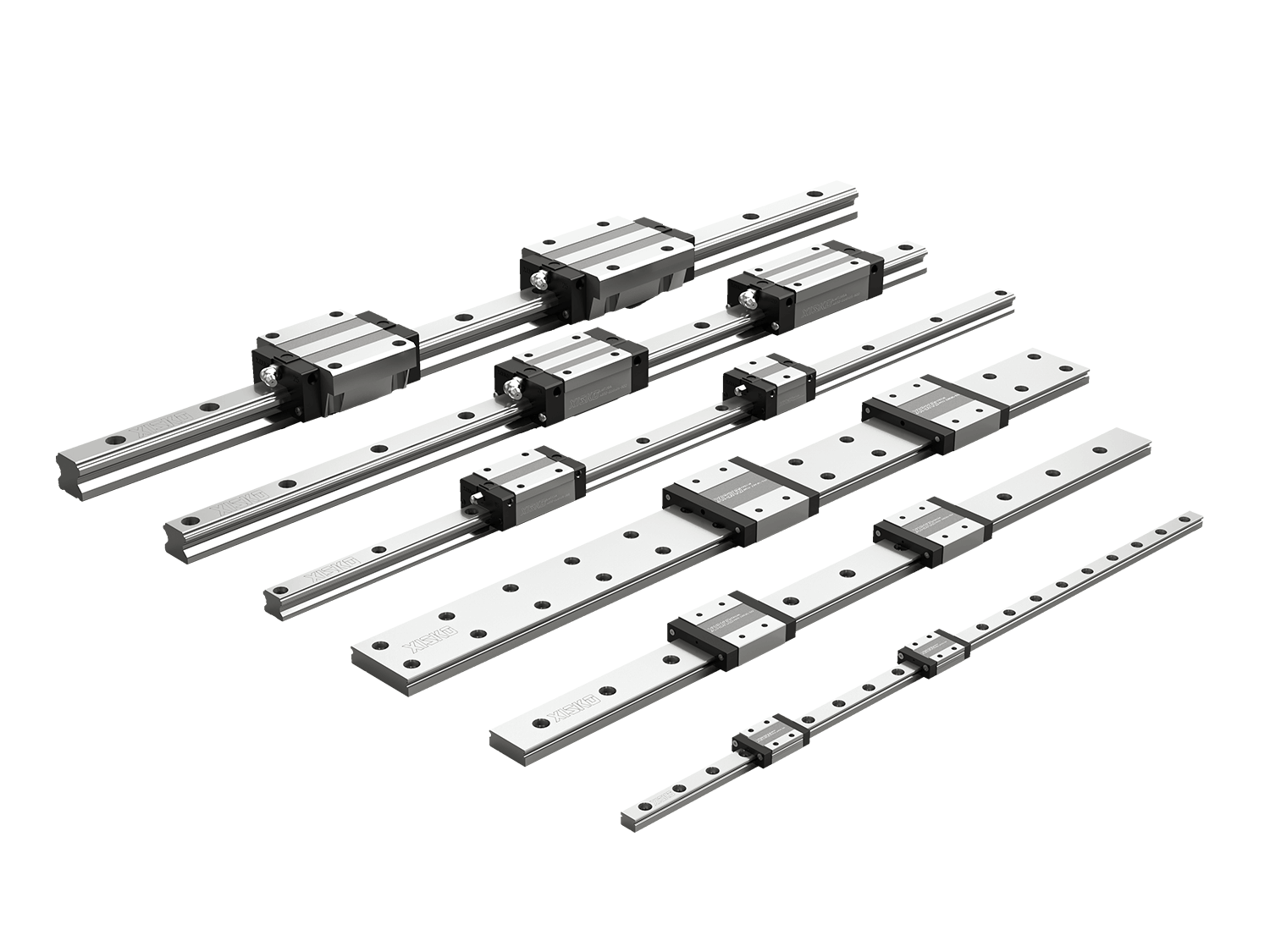
With the continuous advancement of industrial automation, precise, stable, and high-load-capacity transmission components are crucial for optimizing equipment performance. High-assembly ball linear guides, with their excellent load capacity, rigidity, and precision, have become indispensable core components for large-scale automation equipment. This article will comprehensively analyze the structural characteristics, performance advantages, typical applications, and selection criteria of heavy duty linear guides in industrial automation systems to help companies better understand and select these components.
1. What are Heavy Duty Linear Guides?
The LG series linear guides are four-row, single-arc tooth contact linear guides. They incorporate an optimized structural design for ultra-heavy-load precision linear guides, offering improved load and rigidity compared to other linear guides. They are high-load, high-rigidity linear motion guide components designed specifically for industrial applications subject to high torque and shock loads. Its basic structure includes:
- Guide rail body: typically made of high-carbon steel, quenched and precision-machined;
- Slider assembly: consisting of rolling elements, retainers, and sealing systems;
- Rolling element types: common types include ball, roller, and cross-roller;
- Lubrication system: includes an oil cup or can be connected to a centralized lubrication system.
2. Core Advantages of Heavy Duty Linear Guides
2.1 Self-Aligning Capability
The DF (45°-45°) arrangement of the circular grooves allows for the elastic deformation of the steel balls and the shifting of the contact points during installation. Even slight deviations in the mounting surface are absorbed by the linear guide slider, creating a self-aligning effect and achieving high-precision, stable, and smooth motion.
2.2 Interchangeability
Due to strict manufacturing precision control, heavy duty linear guide dimensions are maintained within a certain range. The sliders are designed with retainers to prevent ball loss, resulting in interchangeable precision in some series. Customers can order either rails or sliders as needed, and can also store rails and sliders separately to reduce storage space. High rigidity in all directions.
The four-row circular groove design and four rows of steel balls with a 45-degree contact angle create an ideal two-point contact structure, capable of withstanding loads from both vertical and horizontal directions. Preload can be applied when necessary to enhance rigidity.
2.3 High Load-Carrying Capacity
By replacing balls with rollers, contact becomes linear rather than point, increasing the unit contact area and improving the guide's load-bearing capacity in vertical loads, lateral moments, and torque. It is suitable for applications such as large-tonnage and heavy machinery.
2.4 Long Service Life
The heavy duty linear guide's rolling elements exhibit low contact stress, and coupled with a high-quality sealing system and lubrication system, they maintain a long lifespan and stable operation in harsh industrial environments.
3. Typical Applications
3.1 CNC Machine Tools and Machining Centers
Heavy duty linear guides are the preferred choice for main drive systems in large gantry machining centers, heavy-duty lathes, and five-axis machining equipment, ensuring precise, fast, and stable tool feed.
3.2 Automated Assembly Lines
In continuous production systems such as automobile manufacturing and home appliance assembly, heavy duty guide rails can support robotic arms or fixtures to perform smooth and high-frequency movements, avoiding positioning errors and structural fatigue.
3.3 Injection Molding and Die-Casting Equipment
Equipment with large mold structures and complex motion paths must use high-rigidity guide rails to ensure smooth mold opening and closing and smooth equipment operation.
3.4 Industrial Robot Rails
The heavy duty linear guides required for collaborative or heavy-load robot movement must have high strength and impact resistance. Heavy-duty linear guide rails are an ideal option.
3.5 Metallurgical and Mining Machinery
For example, in large cutting machines and rolling equipment, guide rails need to withstand high temperatures, high dust, and high load environments. The sealing and wear resistance of heavy-duty guide rails are particularly critical.
4. Installation Precautions
4.1 Height and Chamfer of the Mounting Surface Shoulder
When installing heavy duty linear guides, you must pay attention to whether the mounting surface shoulder is appropriate. If the chamfer is too large, the protruding area will easily cause poor linear slide rail accuracy, and if the height is too high, it will interfere with the slider. Therefore, if the surface shoulder can be installed according to the recommended requirements, poor installation accuracy can be eliminated.
4.2 Torque Value of the Guide Rail Assembly Screws
Whether the guide rail is locked tightly against the reference surface during installation has a significant impact on the accuracy of the linear guide rail. Therefore, in order to ensure that every screw is tightened, it is necessary to tighten the guide rail.
Summary
Heavy duty linear guides, as the "skeleton transmission unit" in industrial automation systems, play an irreplaceable role in ensuring equipment stability, improving production efficiency, and reducing failure rates. As the trend of equipment becoming larger and more sophisticated intensifies, the demand for high-performance guide rail systems will continue to grow.