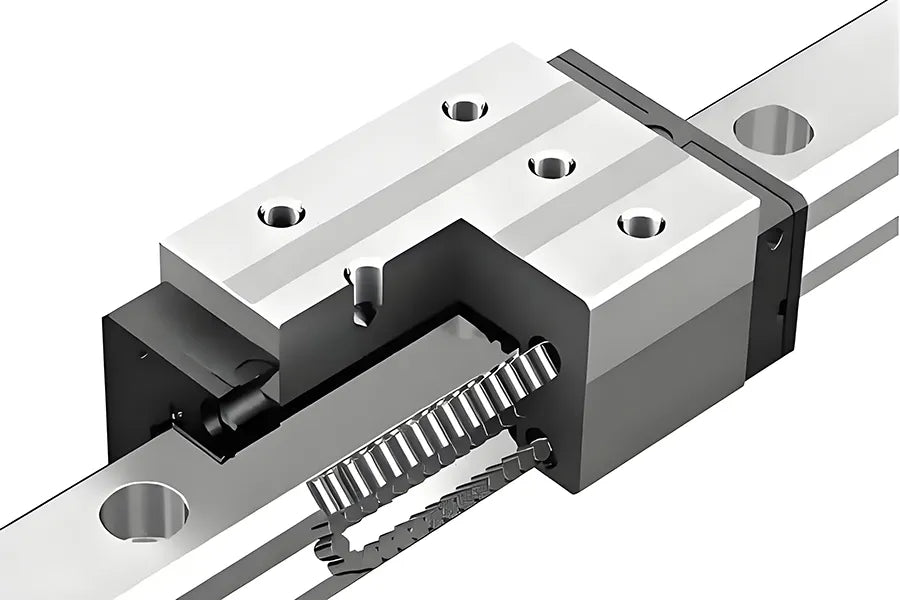
In modern mechanical manufacturing and automation equipment, linear motion systems play a vital role. Among various devices that achieve precise linear motion, linear bearing guide rails are a common and key component. It can not only significantly improve the operating accuracy and efficiency of the equipment, but also has an important impact on the mechanical life, operational stability and smoothness of movement.
1. Linear Bearing Guide Rails
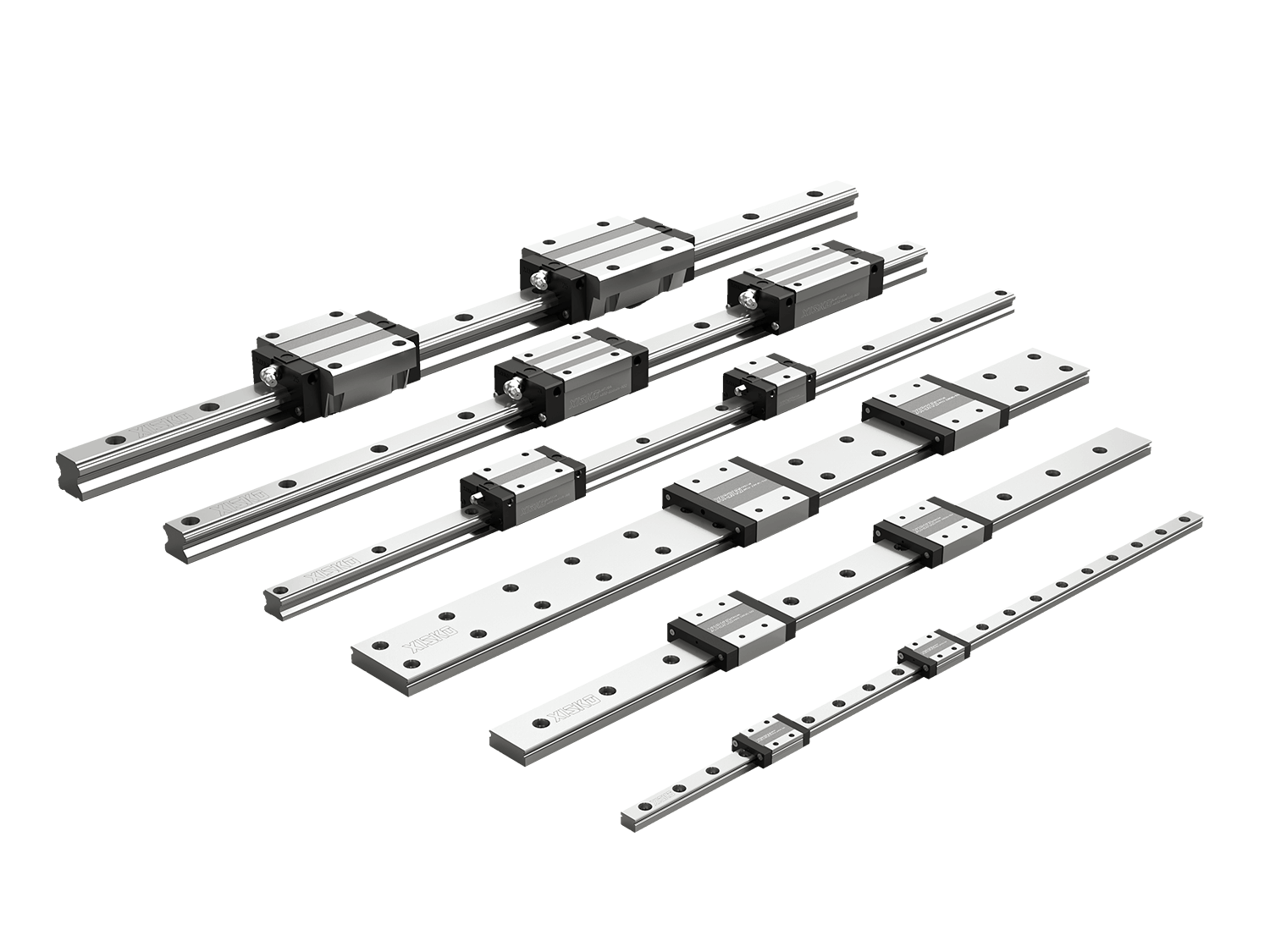
Linear bearing guide rails are a mechanical guide device used to achieve linear motion of objects in a fixed direction. It usually consists of two parts:
- Linear guide rails: As a motion track, it is usually made of high-strength steel with extremely high geometric accuracy and smooth surface.
- Linear bearings or sliders (Linear Bearing/Carriage/Block): The part that moves on the guide rail contains a ball or roller structure to reduce friction and support the load.
Through the rolling or sliding of the bearing on the guide rail, the linear guide rail system can achieve precise linear motion with minimal resistance, and has the advantages of high rigidity, high load and long life.
2. Working Principle
The basic principle of linear bearing slides is to convert sliding friction into rolling friction to reduce the friction coefficient and improve the efficiency of movement.
In the rolling linear guide system, a ball or roller is installed inside the slider. When the slider moves along the track, the rolling body rolls cyclically between the track and the slider. Since the rolling friction is much smaller than the sliding friction, the system runs more smoothly, with higher precision and lower wear.
In addition, in order to ensure long-term stable operation, the slider is usually equipped with a lubrication system and a dustproof device to ensure that the rolling parts are not contaminated by foreign matter and extend the service life.
3. Common Types
3.1 High Assembly Ball-type Linear Guide
The high assembly linear guide is a standard structure with a large guide rail height and a thick slider. The assembly margin between the slider and the track is large, which is convenient for absorbing processing errors.
- Features
Strong rigidity and large bearing capacity, suitable for heavy load occasions;
High stability, suitable for high-precision processing equipment;
Good vibration resistance;
Usually equipped with a self-lubricating system, easy maintenance.
- Application
Widely used in CNC machine tools, machining centers, heavy automation equipment, mold machinery, etc.
3.2 Low Assembly Ball-type Linear Guide
Low assembly type guide is a structure developed to meet the compact design requirements of equipment, with a lower overall height and a center of gravity closer to the installation surface.
- Features
Compact structure, suitable for occasions with limited installation space;
Low center of gravity, improves equipment stability;
Usually the load capacity is slightly lower than the high assembly type, but meets most medium and light load scenarios;
Suitable for fast movement and high dynamic response occasions.
- Application
Automatic feeding device, handling system, testing equipment, light engraving machine, etc.
3.3 Miniature Linear Guide
Miniature linear guide is a guide system designed for small equipment or precision instruments, with the characteristics of small size, light weight and high precision.
- Features
Extremely small size, suitable for micro or precision structures;
Smooth operation, low noise, low friction;
High precision, suitable for micron-level control requirements;
Limited load capacity, suitable for light loads.
- Applications
Optoelectronic equipment, 3D printers, medical instruments, automated experimental equipment, camera module displacement platform, etc.
3.4 Miniature Wide-type Linear Guide
Miniature wide-type linear guide is a design that increases the width of the slider on the basis of the miniature guide, thereby improving its load capacity and anti-torsion performance.
- Features
Wide slider design enhances lateral rigidity and anti-overturning ability;
Also suitable for precision equipment with limited space and high load;
Maintain the low noise and high precision characteristics of the miniature guide;
The installation stability is better than the standard miniature slider.
- Applications
High-precision transfer platform, desktop industrial equipment, optical adjustment equipment, semiconductor devices, etc.
4. Application Fields
With the development of industrial automation and intelligent manufacturing, the application scope of linear guides is becoming increasingly wide, covering almost all scenarios that require high-precision and high-speed linear movement, including:
- CNC machine tools and machining centers
Achieve high-precision relative movement between tools and workpieces to improve machining quality.
- Industrial robots
As a guide device for joints, arms or end effectors, achieve precise positioning and repetitive movements.
- Automated assembly lines and assembly lines
Ensure the efficiency and stability of operations such as material handling and workpiece positioning.
- Medical and testing equipment
Ensure the accuracy and cleanliness of sliding in fields such as X-ray machines, CT equipment, and precision experimental instruments.
- 3D printing and laser engraving equipment
Achieve high-speed, low-vibration, and high-repetition accuracy trajectory control.
- Optical and semiconductor industries
Meet the special needs of dust-free, oil-free, and ultra-high precision.
Summary
As the core component for achieving efficient mechanical linear motion, linear bearing guides have become an indispensable and important part of modern equipment. With its advantages of high precision, high speed, long life and low maintenance, it is widely used in various fields such as industrial automation, precision manufacturing, medical equipment, etc.