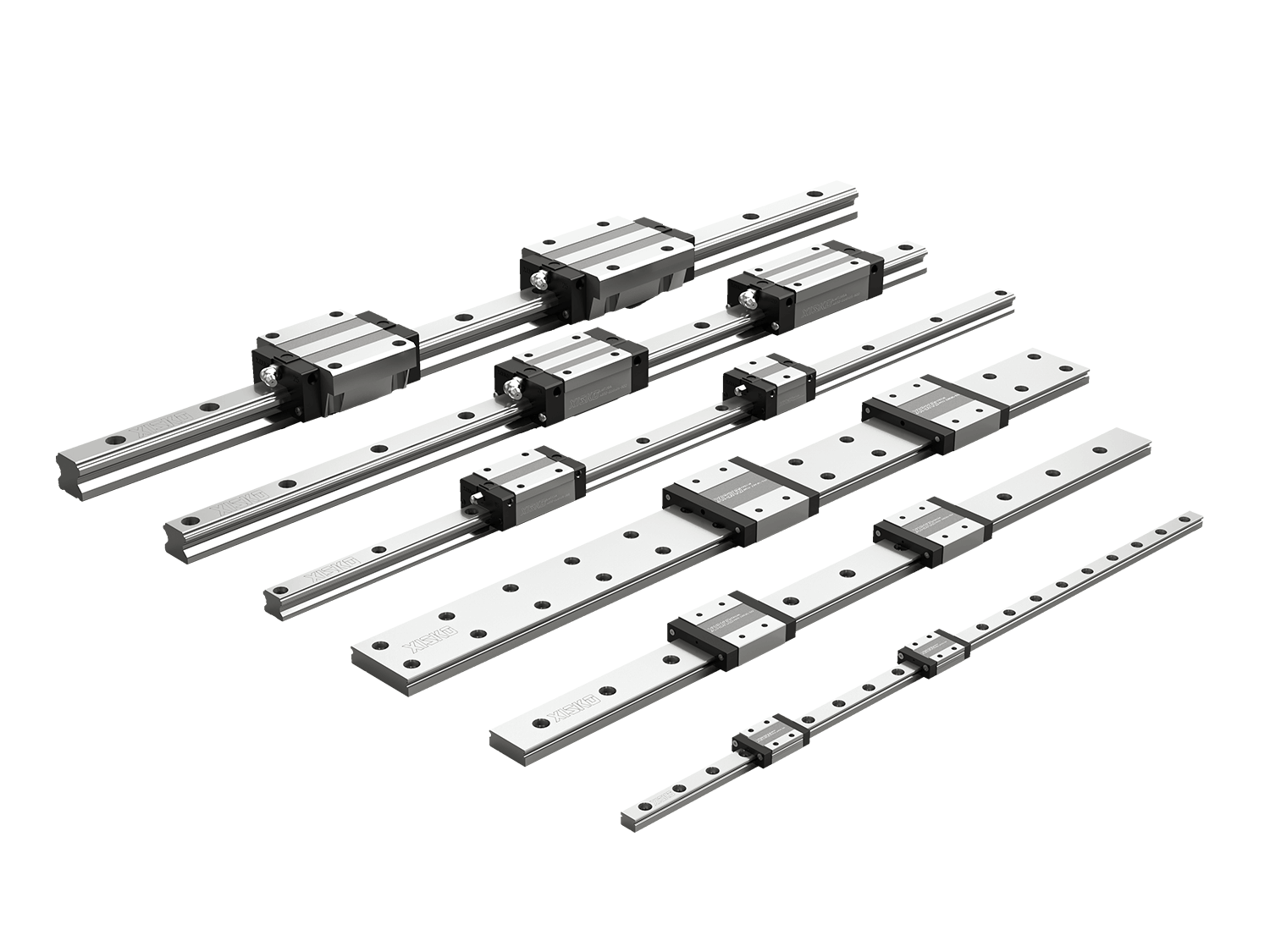
There are numerous types of linear slides available on the market, with varying structural forms, load capacities, and accuracy levels. Choosing the right slide is crucial for achieving the ideal balance between efficiency and cost. This article will provide an in-depth understanding of the main types of linear guides, their advantages and disadvantages, and help you determine which is best suited for your business needs.
1. Main Types of Linear Slides
Simkawa offers a wide range of linear guides to meet the needs of diverse businesses.
1.1 LG Linear Guides
High rigidity and high precision make them suitable for heavy-load equipment and high-precision machining.
1.2 LM Linear Guides
Lightweight design makes them suitable for small and medium-sized machinery and automation equipment.
1.3 LGN Miniature Guides
Compact and compact, LGN linear slides are suitable for micro-machinery and high-precision instruments.
1.4 LGW Miniature Wide Guides
The miniature design combines a wide contact surface with increased load capacity and stability.
1.5 LMGQ Linear Guides
Made with a special resin ball coupling, the LMGQ is quieter than other guide types and is suitable for industrial automation and CNC equipment.
1.6 LMR Linear Guides
Lightweight roller-type linear slides are suitable for heavy-load and high-speed motion.
Simkawa's linear guide series covers a wide range of application requirements, from micro to heavy loads, and from lightweight to high-rigidity, providing precise, stable, and efficient linear motion solutions for your equipment.
2. Features
2.1 Advantages
- Simple structure, easy manufacturing, good rigidity, and strong vibration resistance make them widely used in general machine tools.
- Surface hardening followed by grinding provides high wear resistance and precision.
2.2 Disadvantages
- The guide friction coefficient is relatively high, with the dynamic and static friction coefficients being essentially the same. This results in low starting resistance, excellent low-speed motion stability, high positioning accuracy, accurate micro-displacement, low wear, excellent precision retention, and a long service life.
- Poor vibration resistance requires high protection requirements.
3. How to Choose the Right Linear Guide?
3.1 Considering the Static Safety Factor
When using linear slides in slow motion or high-frequency applications, the static safety factor must be considered. When calculating static load, different safety factors must be considered depending on the application conditions. In particular, a larger safety factor is required when linear guides are subjected to heavy loads.
3.2 Selecting a Safety Factor Based on Load Type
In light-load applications, a lower safety factor can be used. For heavy or impact loads, a larger safety factor is recommended to improve guide life and motion stability.
3.3 Comprehensively Consider the Application Environment
The guide rail's accuracy grade, load capacity, lubrication, and protection design should all be tailored to the actual application environment.
For example, high-speed automation equipment requires low-friction, high-precision guide rails, while dusty or corrosive environments prioritize guide rails with excellent protection.
Summary
When selecting linear slides, comprehensive considerations should be made. Simkawa offers one-stop solutions, from selection and customization to installation and maintenance, tailored to your business needs, to help you achieve optimal performance and reliability in your linear motion system.
FAQ
1. What is the 2:1 Rule for Linear Bearings?
The 2:1 rule states that the distance from the point of application of the driving force to the fixed bearing end cannot exceed twice the fixed bearing length/spacing.
So, we need to understand the following three points:
- The 2:1 rule has nothing to do with load or driving force; it only relates to the coefficient of friction!
- The 2:1 rule should be applied to the fixed bearing end, not the floating bearing end; the floating bearing end only serves as a guide.
- The 2:1 rule is based on a friction coefficient of 0.25; if the friction coefficient changes, this value will also change.
2. Why are Linear Guides so Expensive?
The high price of linear guides is mainly due to their high-precision manufacturing, high-quality materials, complex rolling structure and strict quality control. These ensure the high load capacity, stability and service life of the guides.