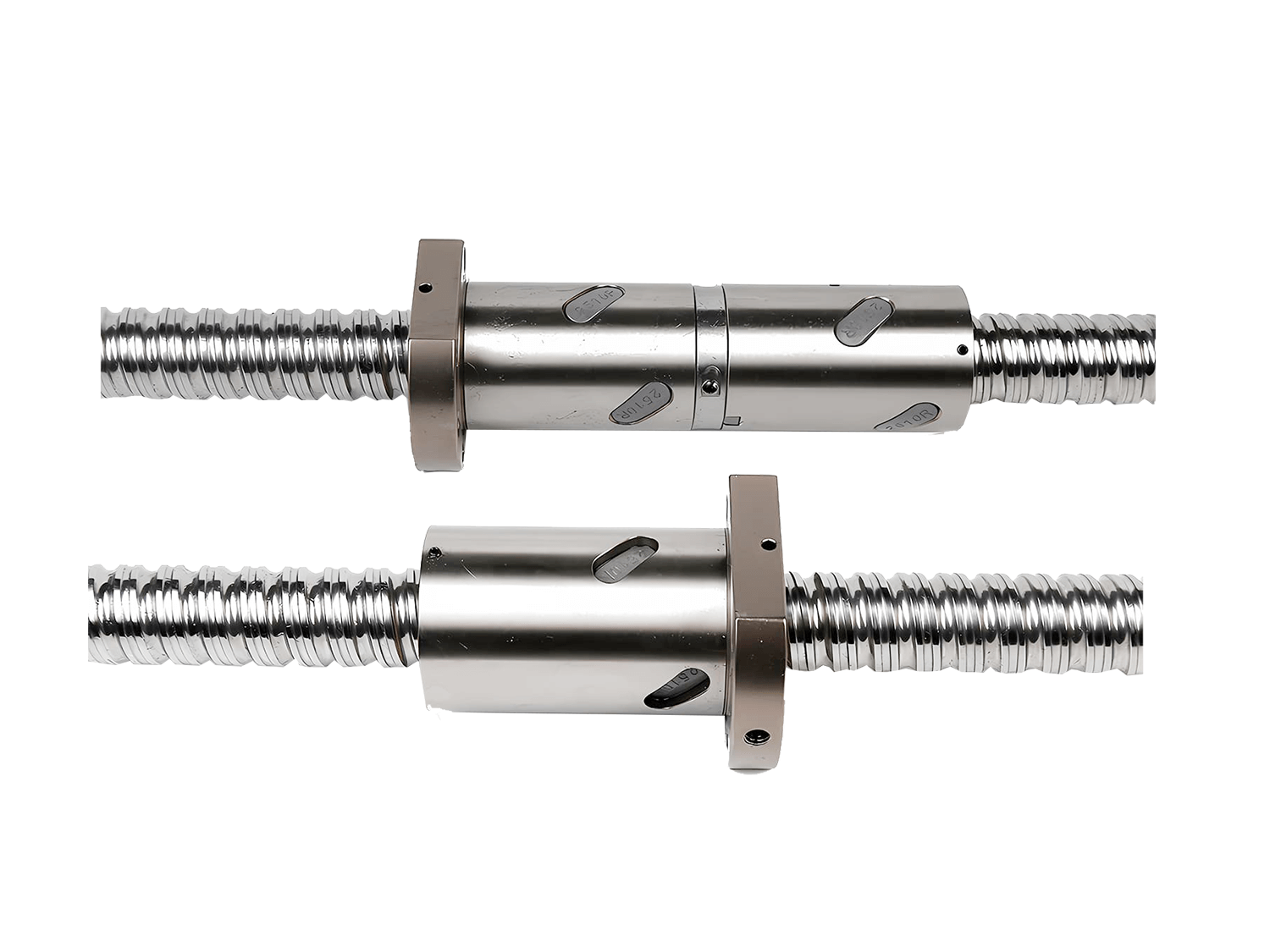
The ball screw linear actuator is a highly efficient transmission mechanism that converts the rotary motion of the motor into precise linear motion. Its core component, the ball screw assembly, achieves high-precision, low-friction linear drive by rolling the balls between the threads. In this process, the ball circulation method is one of the important factors affecting the performance, life and noise level of the actuator.
1. Internal Circulation
In the internal ball recirculation system, the balls are kept inside the nut housing. This design avoids external protrusions and makes the internal ball nut more compact. And because the recirculation only occurs inside the nut housing, the system generates less noise and vibration. This type of ball screw includes deflection type and end cover type.
1.1 Deflection Ball Screw
The deflector guides the balls across the diameter of the screw shaft back to the adjacent groove. Each turn of the screw requires a deflector to complete the ball path. This design is very suitable for applications that require fine lead and has a compact structure, allowing the design of multiple independent circuits.

1.2 End Cap Ball Screws
The end cap guides the balls back to their starting point through a channel inside the nut. This design is particularly suitable for high-lead ball screw applications because it can withstand the forces generated by the rapidly moving balls.

2. External Recirculation
In an external ball recirculation system, the balls travel outside the nut shell. This system supports fine lead components and can adapt to a variety of screw shaft diameters. It is cost-effective and suitable for large-scale production, but it increases the overall size. Only return tube ball screws use this system. Another way to classify ball screws is based on the different manufacturing methods:
2.1 Ground Screw Threads
Ground screw threads are produced by a grinding process. In this method, the blank shaft is placed horizontally and then grooves are carved out using a very hard grinding tool. Compared with rolled screws, this process produces a smoother groove surface and higher precision, but it is more expensive and slower to produce.

2.2 Return Tube Ball Screws
In an external ball recirculation system, the balls run from the wall of the ball nut through a protruding external tube. This return pipe guides the balls back to their starting point. The finger-shaped part connected to the end of the return pipe guides the balls as they enter and exit the pipe. The length of the return pipe is supported by a pipe fixing bracket, making the return pipe assembly easy to install and remove.

2.3 Rolled Ball Screws
Rolled threads are manufactured by cold working deformation. The uncut blank shaft passes through a rotating tool die to form a groove. This process causes significant plastic deformation in the blank, resulting in a high-strength screw. Although this method is more economical and simple to manufacture than ground screws, it produces a rougher surface. Due to the increased friction, the efficiency and wear resistance of the ball screw linear actuator are also reduced.

3. The Difference Between the Two
| Comparison | Internal Circulation | External Circulation |
| Compact structure | More compact structure, takes up less space, suitable for precision equipment | Relatively complex structure, takes up more space |
| Load Capacity | Medium load capacity for light and medium load applications | High load capacity for high load systems |
| Noise Control | Low operating noise, smooth ball bearing steering | Slightly noisy, requiring additional lubrication or silencer measures |
| Applicable Stroke | Suitable for short to medium stroke applications | Can achieve medium to long stroke motion |
| Maintenance Difficulty | The internal structure is complex, making maintenance difficult. | The external circuit is visible, making inspection and replacement easier. |
| Protective performance | Good sealing, strong dust and dirt resistance | Many exposed parts require additional protective design |
4. How to Choose the Appropriate Ball Screw Circulation Method?
When selecting a ball screw linear actuator, the following factors should be considered:
- Installation Space: When space is limited, the internal circulation structure is preferred.
- Load Requirements: External circulation is recommended for high-load, high-thrust systems.
- Operating Noise: Internal circulation is better for precision equipment with high quiet requirements.
- Maintenance Ease: If the equipment requires regular maintenance or component replacement, external circulation is easier to operate.
Selecting the appropriate circulation method not only improves equipment performance but also extends system life and reduces operating costs.
Summary
In practical applications, understanding the structural characteristics of different circulation methods will help engineers customize more efficient linear motion solutions based on their needs. Whether using internal or external circulation, the circulation system of a ball screw linear actuator is a key factor affecting its operational stability and accuracy.