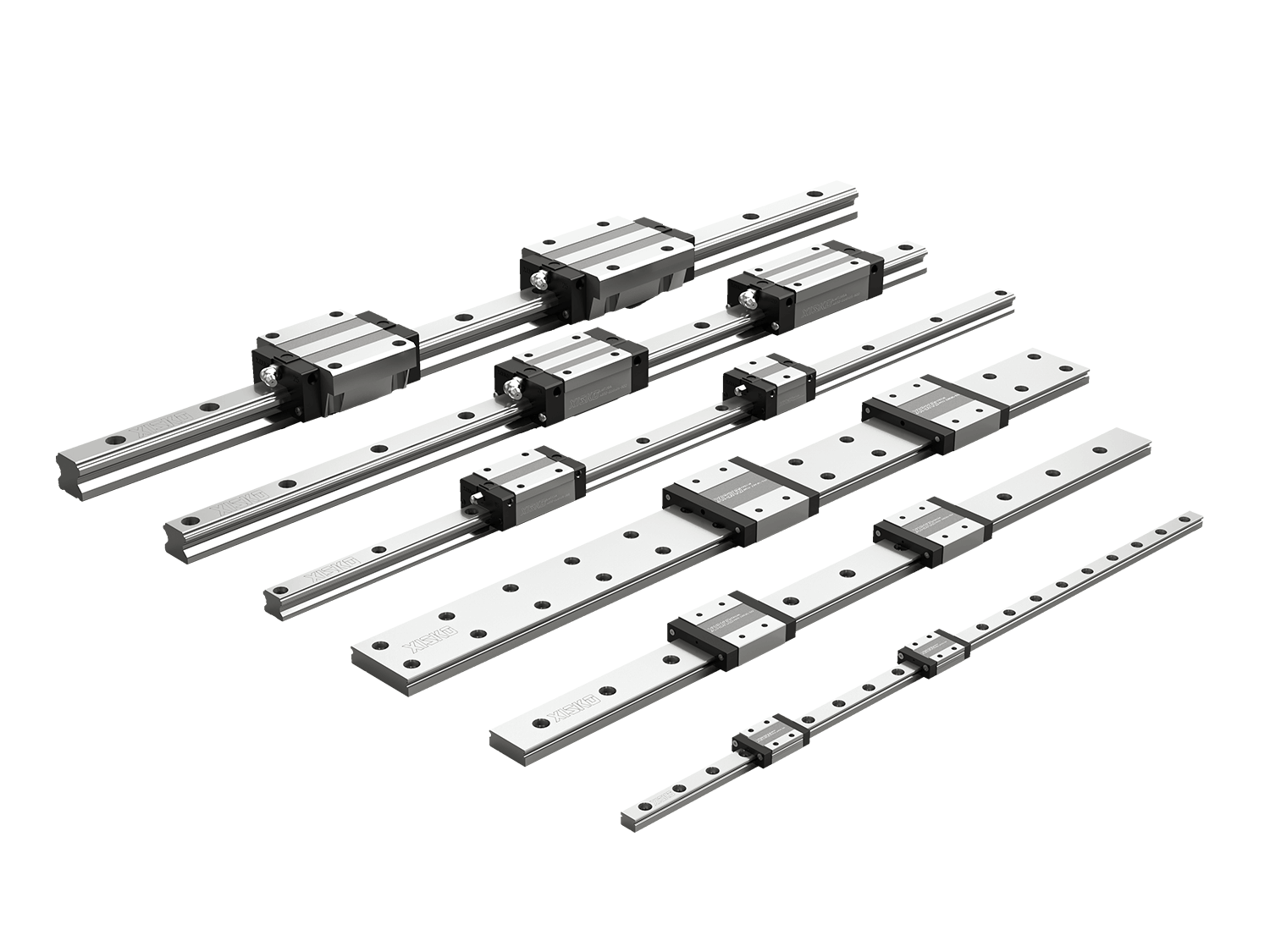
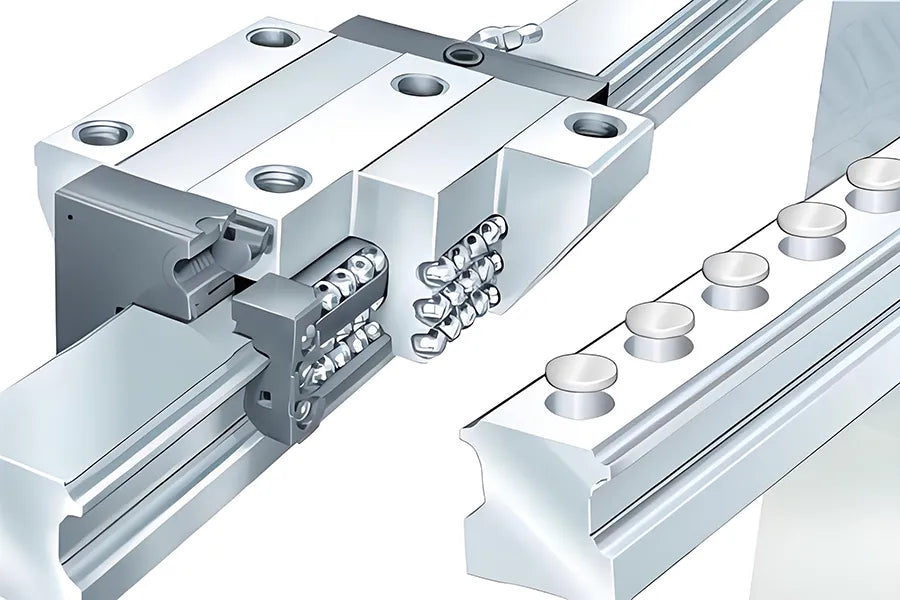
In linear motion systems such as industrial automation, CNC machine tools, robots, and medical equipment, guide rails are crucial transmission components. According to different structures and application scenarios, guide rails can be roughly divided into circular guide rails (circular/round rails) and linear guide rails (linear guide/linear rails). So, what is the difference between them?
1. What is a Circular Guide Rail?
A circular guide rail is a linear motion component that uses a cylindrical steel shaft as a guide rail and runs with a circular slider or bearing sleeve. Common forms include: cylindrical guide rail + linear bearing sleeve (such as LM type bearing), support guide rail with fixed seat, etc.
Main features
Large installation tolerance and strong adaptability
Relatively low cost
Self-alignable, suitable for occasions with low alignment requirements
Strong adaptability to polluted environments (such as dust and debris)
2. What is a Linear Guide Rail?
Linear guide rails (also called linear slide rails) are usually rectangular structures, consisting of a high-precision guide rail and a set of sliders. The sliders are equipped with steel balls or rollers for cyclic rolling to achieve low-friction, high-precision linear motion.
Main features
High positioning accuracy, repeatability can reach micron level
High rigidity, suitable for carrying high loads
Compact structure, guide rails can be directly installed on mechanical structures
Commonly used in systems with high requirements for accuracy, speed and rigidity
3. How to Choose the Appropriate Type of Guide Rail?
When choosing the type of guide rail, it is recommended to consider the following aspects comprehensively:
3.1 Requirements for accuracy
If the application scenario requires high repeatability and high positioning stability (such as CNC machining, visual positioning platform, etc.), linear guide rails should be given priority.
3.2 Is the working environment harsh?
Circular guide rails are more stable in dusty, oily, and debris-rich environments, and are not easy to get stuck. They are suitable for woodworking machinery, conveying systems, etc.
3.3 Is it necessary to install easily?
Circular guide rails have low requirements for mounting surface accuracy and are suitable for systems with rapid deployment or limited site conditions. Linear guide rails need to be processed to flatten the mounting reference surface.
3.4 Budget and cost-effectiveness
If the project budget is limited and the accuracy requirements are moderate, you can choose economical and practical circular guide rails. If you pursue optimal performance and the lowest failure rate, choosing linear guide rails is more valuable in the long run.
3.5 Space limitations and load size
When the space is small but high load is required, narrow linear guides or roller guides can be used; when the space is ample and the load is light, circular guides can do the job.
4. Application Example Comparison
4.1 Circular guides
Automatic feeding mechanism
Non-critical positioning components in medical instruments
3D printers and light-load slides
Packaging and labeling equipment
4.2 Linear guides
XYZ platforms of CNC machine tools
Laser cutting and marking equipment
Automatic assembly line positioning mechanism
Industrial robot joint module
Summary
Although both circular guides and linear guides are linear transmission components, they differ significantly in structural design, performance, installation requirements and applicable scenarios.