As the manufacturing industry develops rapidly towards high precision, high efficiency and intelligence, CNC machine tools are becoming more and more important in modern industry. As one of the key linear motion components in CNC machine tools, linear guide rails play an irreplaceable role in improving processing accuracy, stability and operating efficiency. This article will explore in depth the application, types, advantages and future development trends of linear guide rails in CNC machine tools.
1. What is a Linear Guide Rail?
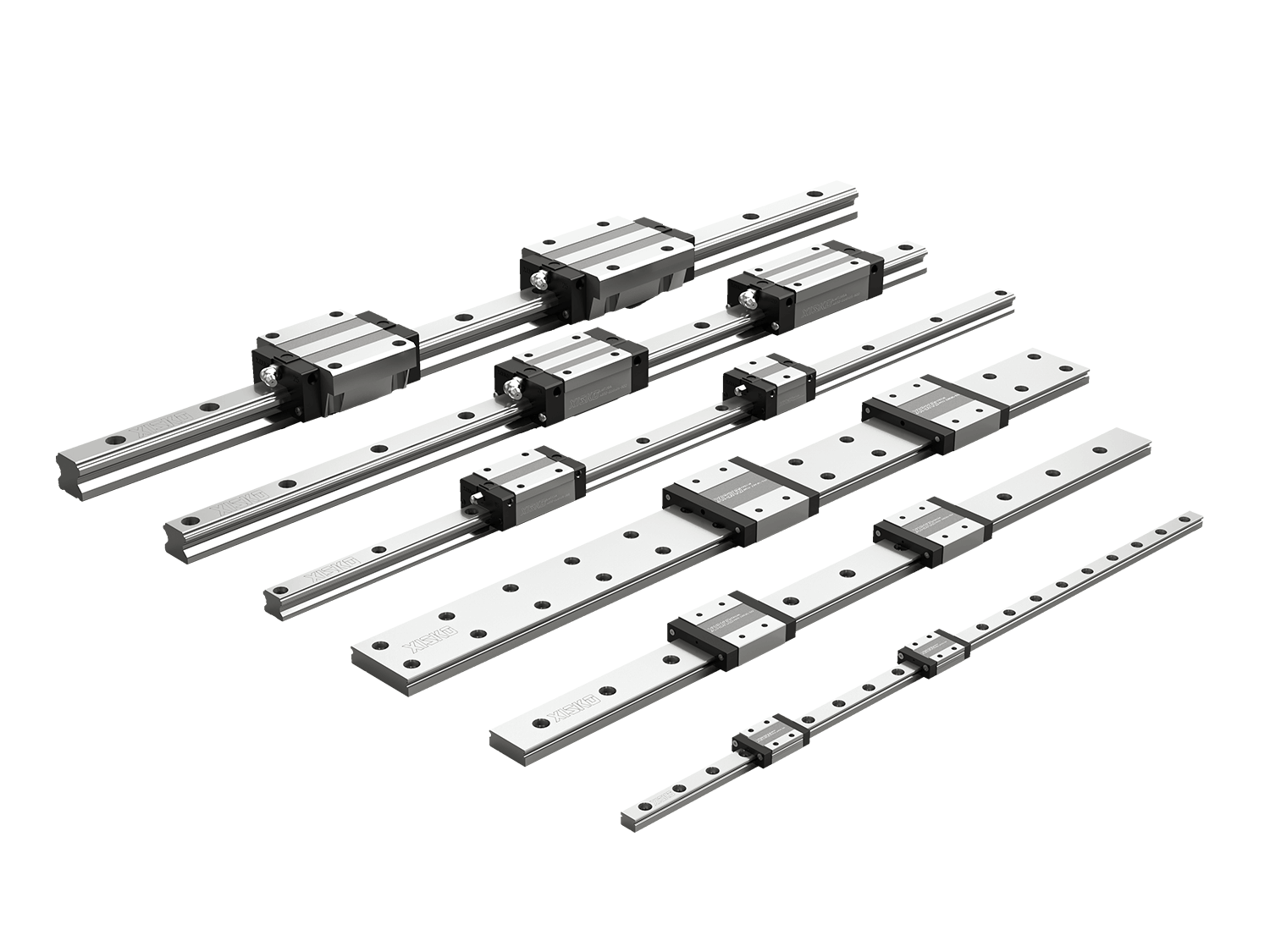
Linear guide rails, also known as linear slide rails, are mechanical elements used to carry and guide moving parts to move in a straight line. Compared with traditional sliding guide rails, linear guide rails use rolling friction to make the movement process smoother and more precise. Its typical structure includes guide rails, sliders, rolling elements (steel balls or rollers), dust and lubrication systems, etc.
In CNC machine tools, linear guide rails are mainly used for high-precision linear displacement of components such as spindle tables, workbenches or turrets.
2. Main Application
2.1 Workbench sliding system
In CNC milling machines or machining centers, the linear movement of the three axes X, Y, and Z is usually achieved by linear guides. The rigidity and precision of the guides directly determine the machining stability and repeatability of the machine tool.
2.2 Spindle feed system
In some high-precision CNC lathes or drilling machines, the linear feed movement of the spindle head is achieved through guides, which ensures stable cutting force and low vibration.
2.3 Turret and tool changer
The lateral or longitudinal movement of the turret often relies on linear guides to ensure the rapidity and repeatability of tool replacement.
2.4 Automatic loading and unloading system
In CNC systems with automated robotic arms or workpiece handling functions, linear guides are also commonly used in mobile devices, such as silos, conveyor tables, etc.
3. Advantages of Linear Guides
High precision and high repeatability
The friction coefficient of rolling guides is extremely low, and can achieve micron-level precision, which is suitable for CNC machining scenarios with extremely high requirements for repeatability.
High rigidity and load-bearing capacity
The double-row steel ball or roller design gives the guide rail excellent bending rigidity and impact resistance, can withstand multi-directional loads, and improve the overall structural stability.
High-speed and low-noise operation
Low friction and smooth movement are suitable for high-speed displacement applications; coupled with reasonable lubrication and dust-proof design, the operating noise is effectively reduced.
Easy installation and strong interchangeability
Modern guide rails usually have good interchangeability, which is not only easy to maintain and replace, but also greatly reduces the difficulty of assembly and adjustment time.
Long life and low maintenance cost
Linear guide rails made of high-hardness materials and closed lubrication systems have extremely long service life and long maintenance cycles under correct use, reducing the cost of the entire life cycle of the equipment.
4. Linear Guide Types and Selection
According to the rolling element type and structural design, linear guides are divided into the following categories:
High assembly ball linear guide: The guide and slider are high, and the slider mounting surface is far away from the reference surface, which is suitable for medium-speed and medium-load machine tools;
Low assembly ball linear guide: Compared with the high assembly type, the overall height is lower and closer to the mounting surface. It is often used in systems with limited space or high requirements for equipment center of gravity control.
Micro linear guide: used for compact CNC equipment or high-precision instruments;
Wide or double-track guide: enhance rigidity and improve load stability, commonly used in heavy-duty machining centers.
In the selection process, the guide accuracy grade (such as C, H, P grade), installation method (locking type, flange type), lubrication method, load direction, stroke length and other factors should be considered comprehensively.
Conclusion
As the core component for high-precision and high-efficiency motion control in CNC machine tools, the performance of linear guides is directly related to the overall processing quality and service life of the machine tools.