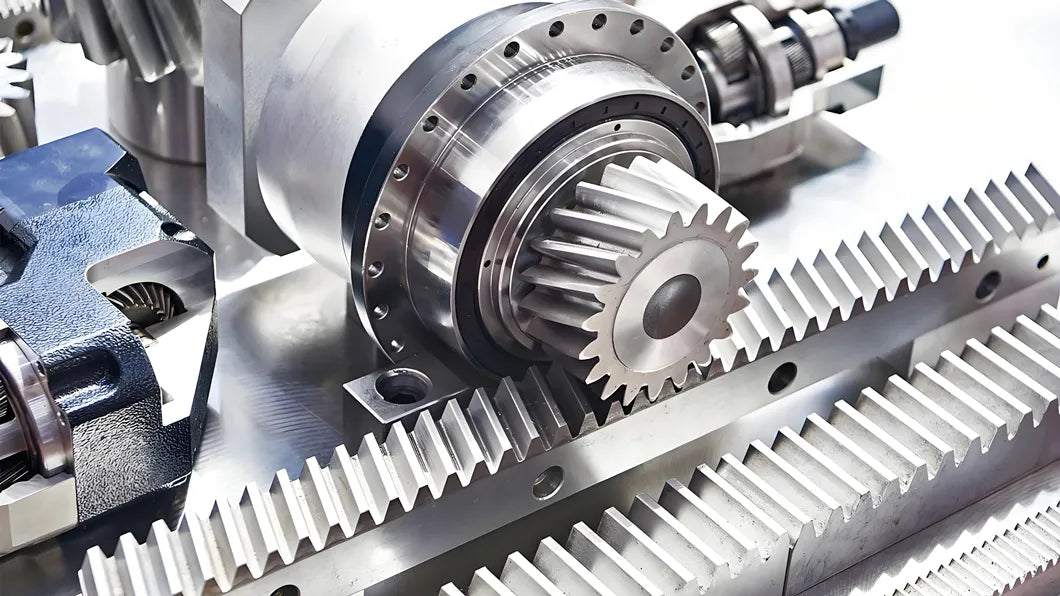
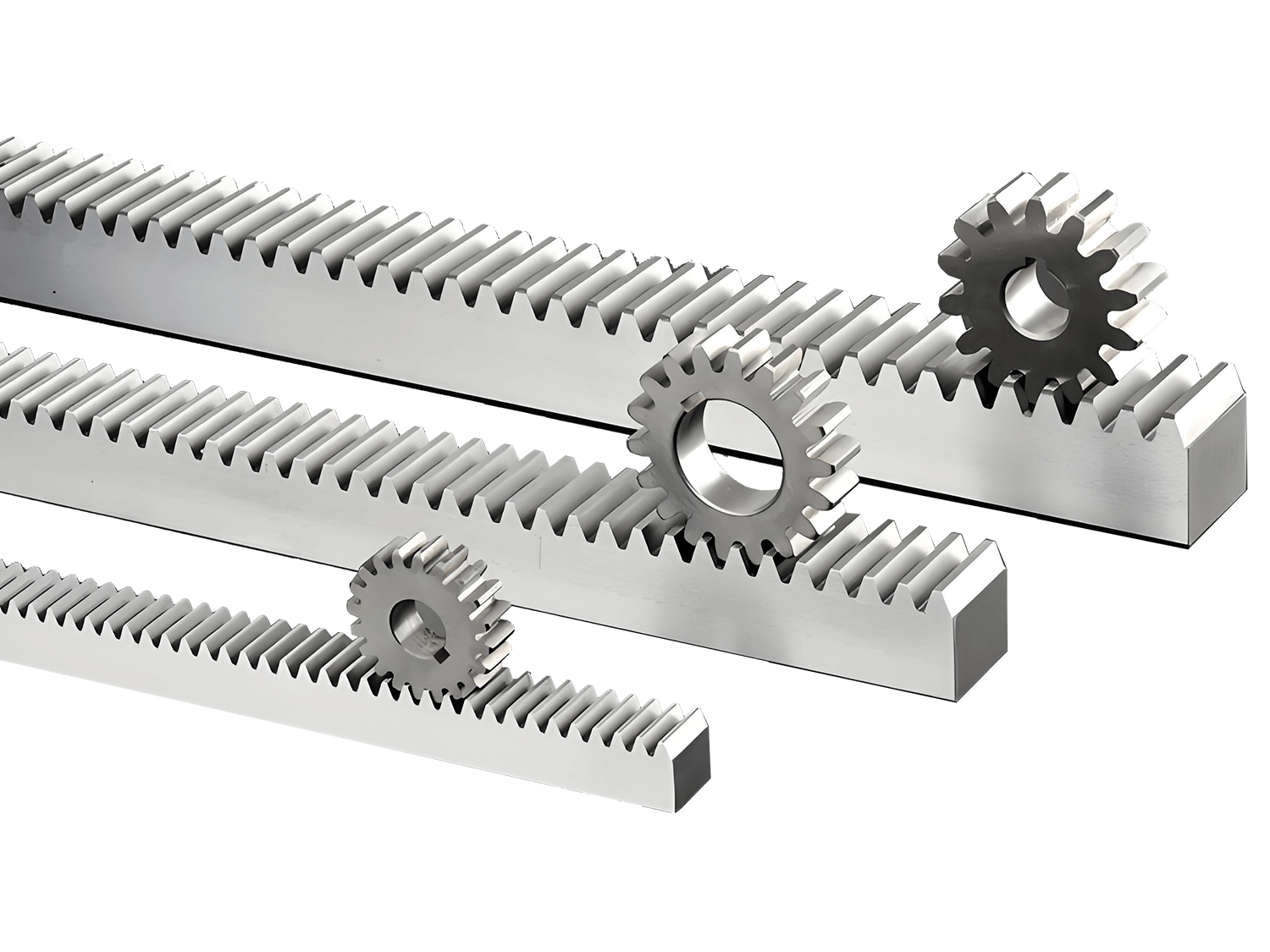
In modern industrial manufacturing and automated production, high-precision linear motion is a key factor in ensuring equipment stability and product quality. With the increasing popularity of CNC machine tools, robots, laser cutting machines, and automated warehousing equipment, rack and pinion transmissions have gained widespread application as efficient and reliable linear motion solutions. CNC gear racks, with their high precision, durability, and flexible applications, have become a key choice for various linear drive systems.
1. Characteristics of Rack and Pinion Transmissions
- Compact Structure: The transmission system consisting of a CNC gear rack has a simple structure and takes up little space.
- High Mechanical Efficiency: Efficiency can reach 0.95-0.99, making it more energy-efficient than solutions like lead screws and chains.
- High Load Capacity: Suitable for high loads and heavy duty applications, it is commonly used in machine tools and heavy machinery.
- High Transmission Accuracy: Positioning accuracy can reach 0.1mm, meeting high-precision motion requirements.
- Infinite Extension: Racks can be spliced together, theoretically enabling infinite linear motion.
- High-Speed Transmission: Speeds exceeding 2m/s are possible, making it suitable for high-speed applications such as laser cutting machines and automated production lines.
2. Comparison of Spur and Helical Gears
| Gear Type | Meshing Line | Advantages and Disadvantages | Applicable |
| Spur Gears | Parallel Lines | Simple machining, no axial force component, but poor stability and vibration | Ordinary |
| Helical Gears | Helical Line | Difficult machining, axial force, but good stability and low vibration | High speed and heavy load |
3. CNC Gear Rack Materials
Common gear materials include: 42CrMo, 45# steel, SUS304 stainless steel, and engineering resin.
- 42CrMo: Hardness of HRC55-60 after high-frequency heat treatment (high-frequency quenching). The tooth surfaces are ground and suitable for high-intensity working conditions.
- 45# steel: Cost-effective, hardness of HRC50-55 after quenching. The tooth surfaces are finely ground and commonly used in general machinery.
- SUS304: Corrosion-resistant, suitable for specialized industries such as food machinery and medical equipment.
Common rack materials include: 45# steel, SUS304, and resin.
- 45# steel: A common choice with high cost-effectiveness and excellent hardness and wear resistance.
- SUS304: Used in rust- and corrosion-resistant environments.
4. Gear and Rack Accuracy
CNC gear rack accuracy is generally classified into 13 levels (0-12), with level 0 being the highest accuracy. Common accuracy grades: Grade 6 to Grade 8.
Application Accuracy: After assembly, a module 2 rack can achieve positioning accuracy of:
0.03mm (Grade 6), 0.05mm (Grade 8).
This makes it widely used in CNC machine tools and automation equipment.
5. Commonly Used Key Parameters for Gear Racks
Module (m)
Indicates the size of the gear and determines the meshing conditions between the gear and the rack.
Formula:
Pitch diameter: d = mz
Circumference: L = πd
Tooth pitch: p = πm
The larger the module, the greater the tooth pitch, tooth thickness, and tooth height, and the greater the load-bearing capacity.
Common modules: 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6, etc.
Pressure angle (α)
The angle between the normal force and the tangent at any point on the involute.
Common pressure angle: 20° (international standard). Pitch Circle Diameter (d)
Formula: d = mz
This parameter determines the size of the gear and is a key factor in design and selection.
6. Gear Failure Modes
Gear racks may experience the following failures over long-term operation:
- Breakage: Caused by overload or material fatigue.
- Wear: Caused by insufficient lubrication or impurities.
- Pitting: Caused by excessive contact stress on the tooth surfaces.
- Sticking: Adhesion of metal surfaces due to high-temperature friction.
- Plastic deformation: Tooth profile changes caused by excessive impact loads.
7. Comparison with Other Transmission Methods
- Compared to synchronous belt drive: CNC gear racks offer higher precision, longer transmission distances, and greater load-bearing capacity.
- Compared to lead screw drive: Racks are suitable for long travels and high loads, while lead screws are more suitable for short travels and ultra-high precision applications.
- Compared to chain drive: Racks offer higher precision and faster speeds, while chains are more suitable for low-speed, high-torque conditions.
Summary
As a high-precision linear motion solution, CNC gear racks have become a core transmission component in modern manufacturing and automation due to their strong load-bearing capacity, high precision, easy maintenance, and wide application.