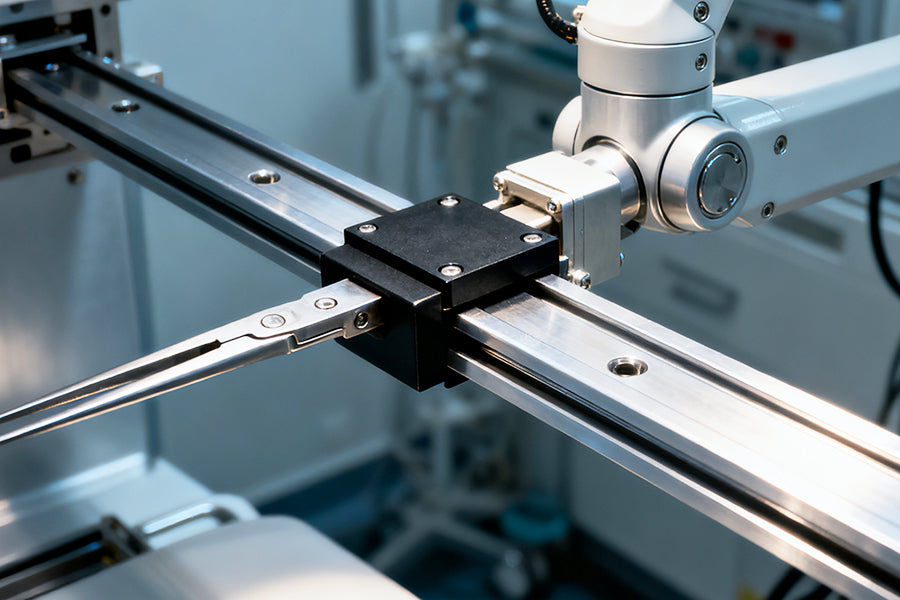
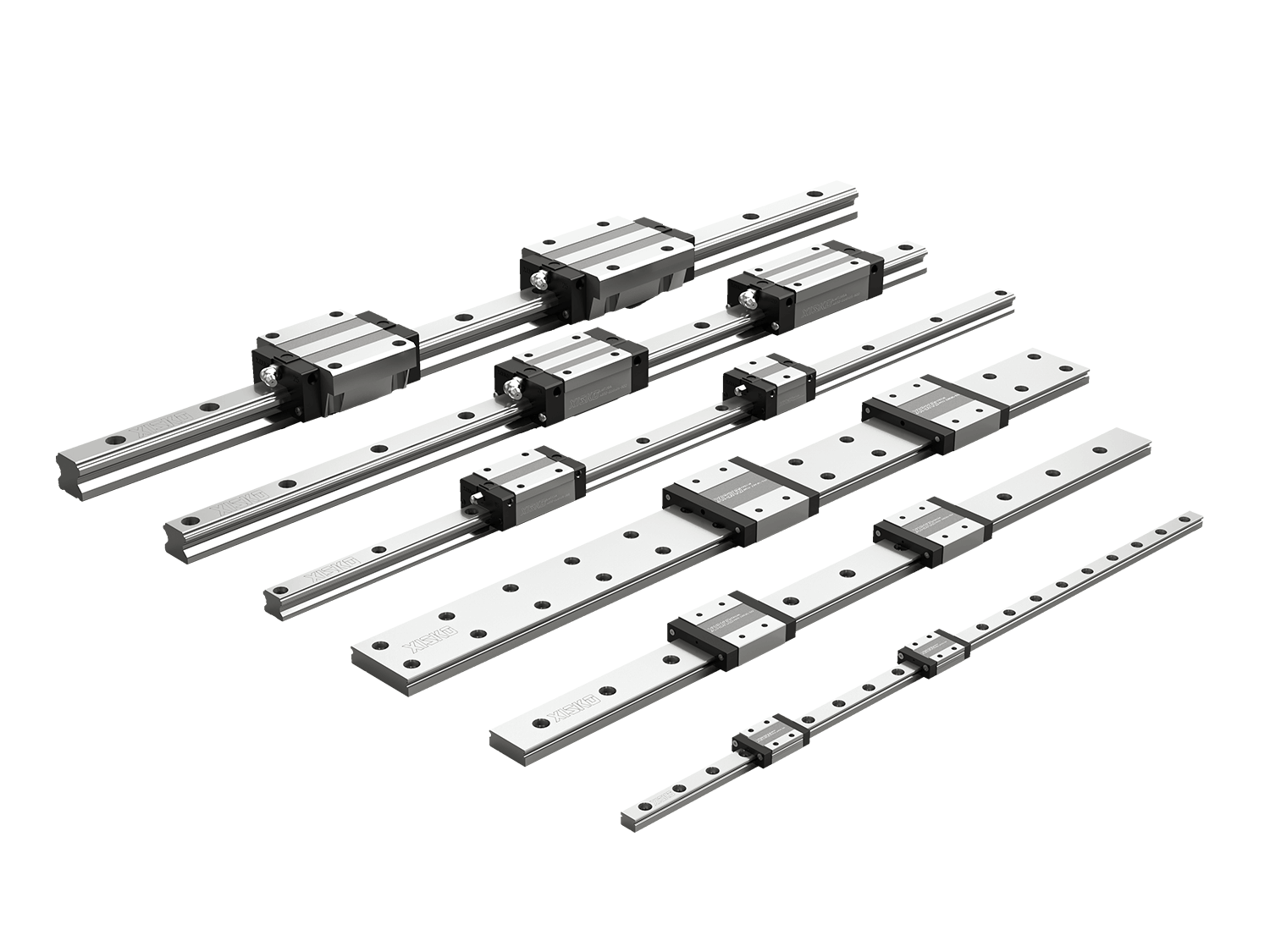
LM rail guides, also known as linear rails, slide rails, or linear guideways, are used in high-precision or high-speed linear reciprocating motion applications. They can withstand a certain amount of torque and achieve high-precision linear motion under high loads.
1. What is an LM Rail Guide?
LM rail guides (linear motion guides) are like invisible highways for mechanical equipment. They achieve linear reciprocating motion through the precise rolling of balls or rollers on the track. Compared to traditional sliding guides, their core advantage lies in replacing sliding friction with rolling friction, thereby significantly reducing running resistance, improving motion accuracy, and maintaining stable repeatability during high-speed, long-term operation.
2. Core Features of LM Linear Guides
The widespread use of LM low-assembly ball linear guides in various industries stems primarily from their excellent structural advantages, including:
2.1 Four-row ball bearing structure
The four-row ball bearing design allows for load bearing from multiple directions, providing high rigidity and high load capacity, making it suitable for high-speed automated equipment requiring stable support.
2.2 Four-Directional Equal Load Capacity
Provides equal load capacity in all four directions (up, down, left, and right), ensuring stable and precise operation even under complex motion conditions.
2.3 Self-Alignment Function
LM rail guide features self-alignment capability, absorbing minor errors in the mounting surface, reducing assembly difficulty, and ensuring overall motion accuracy.
2.4 Low Assembly Height and Short Slider Design
Compact structure with reduced overall height and shortened slider length, ideal for high-speed automated machinery, compact equipment, or space-constrained environments.
2.5 Ball Ball Retainer Design to Prevent Ball Dislodgement
An internal ball ball retainer prevents balls from falling out even during slider disassembly, improving assembly safety and maintenance convenience.
2.6 Interchangeability
Interchangeable products of the same specification allow for slider or guide rail replacement without remachining the base, reducing maintenance costs and increasing equipment flexibility.
3. Product Specifications
The LM rail guide series is divided into two types of linear guides: non-interchangeable and interchangeable. Both types have the same dimensions. The main difference is that the sliders and rails of the interchangeable type can be used interchangeably, which is more convenient. However, the combination accuracy of the interchangeable type cannot reach the ultra-precision level of the non-interchangeable type.
Nevertheless, since the combination accuracy of the Simkawa interchangeable type has reached a certain level, it is a convenient choice for customers who do not need to install paired linear guides. The product specifications of the LM rail guides mainly indicate the dimensions, type, accuracy class, preload, and other specifications to facilitate confirmation of the product by both parties during ordering.
4. Applications of Linear Guides in Automation
In automation equipment, CNC machine tools, industrial robots, automated assembly lines, and material handling systems are the most common applications of linear guides.
4.1 CNC Machine Tools
CNC machine tools are one of the important application areas of LM rail guides. In CNC machine tools, linear guides are used to support and guide the movement of tools or workpieces, ensuring the accuracy and stability of the machining process. Linear guides are ideal for CNC machine tools and other equipment requiring extremely high precision and stability due to their high precision, high rigidity, and high load capacity.
4.2 Industrial Robots
Industrial robots require high-precision positioning and movement apabilities when performing various complex tasks. LM rail guides provide stable support and precise guidance, enabling the robot's end effector to accurately reach its designated position. Therefore, linear guides are widely used in the joints and arms of industrial robots.
4.3 Automated Assembly Lines
On automated assembly lines, various components need to be assembled with high precision and efficiency. LM rail guides ensure the stability and accuracy of components during transport and assembly, thereby improving assembly quality and efficiency. Furthermore, linear guides can withstand large loads, making them suitable for assembling various heavy components.
4.4 Material Handling Systems
Material handling systems are an important component of automated production lines. Linear guides play a crucial role in material handling systems, ensuring the stability and accuracy of materials during transport and preventing material deviation or drop. Meanwhile, the high load-bearing capacity of linear guides allows them to withstand the weight of large amounts of materials, ensuring the smooth completion of handling tasks.
Summary
LM rail guides have broad application prospects in automated equipment. With the continuous development of automation technology, linear guides will leverage their unique advantages in more fields, providing more stable, precise, and efficient support and guidance for automated production.